|
Albania |
Benin |
Egypt |
Kosovo |
|
Peru |
Switzerland |
Algeria |
Bolivia |
|
Finland |
Latvia |
Philippines |
Syria |
|
Angola |
Brazil |
France |
Luxembourg |
|
Portugal |
Turkey |
Antigua & Barbuda |
Bulgaria* |
|
Germany* |
Malawi |
Romania |
United Kingdom |
|
Argentina |
Canada |
Greece |
Malta |
|
Russia |
Vanuatu |
Armenia |
Chile |
|
Hungary |
Mexico |
Serbia |
United States of America |
|
Australia |
Costa Rica |
Iceland |
New Zealand |
|
Slovenia |
Barbados |
Croatia* |
Ireland |
|
Nigeria |
South Africa |
Bangladesh |
Cyprus |
|
Israel |
Norway |
South Korea* |
Belgium |
|
Czech Republic |
Italy |
Pakistan |
Spain |
|
Belize |
Denmark |
Jamaica |
Panama* |
|
Sweden |
United Arab Emirates |
Protecting Assets and Expanding Freedom with Dual Citizenship. We provide guidance on how to obtain multiple citizenships and highlight which countries allow it, enabling you to take full advantage of the benefits. We explain how to properly obtain multiple citizenships and which countries allow it, so you can take advantage of all the benefits.
For many, holding citizenship in multiple countries is a lifelong dream. Having a second home opens up additional opportunities and provides greater freedom for planning in case of emergencies.
This is especially crucial for investors seeking to protect their assets, expand international investments, and provide optimal opportunities for their children’s education and career.
What is dual citizenship, and how can you obtain it? What advantages does it offer? Which countries allow you to hold multiple passports? You will find answers to these questions in our article.
What is Dual Citizenship?
Dual citizenship is a status in which a person is simultaneously a citizen of two or more countries. This allows them to have rights and obligations associated with the citizenship of each country.Dual citizens enjoy rights and privileges, including the ability to work, study, and access healthcare in both countries, as well as be required to comply with laws and pay taxes in those countries.
Many countries do not allow dual citizenship, but the vast majority of countries in the world provide their citizens with the opportunity to apply for and hold a passport from a foreign state.
Some countries, such as Spain, permit dual citizenship under certain circumstances. Spain allows its citizens to acquire citizenship only from specific Latin American countries.
On the other hand, other countries, such as China, India, and Saudi Arabia, do not recognize dual citizenship. These countries automatically revoke the citizenship of their nationals if they acquire citizenship from another country. Moreover, in China and Saudi Arabia, acquiring another citizenship without first renouncing the original citizenship may be considered a criminal offense.
What Differentiates Dual Citizenship from Multiple Citizenship?
Obtaining citizenship from more than two countries is based on the same principles as dual citizenship. Multiple citizenship allows a person to hold citizenship in several countries simultaneously, providing significant freedom of movement, such as the ability to travel visa-free, and offers full financial freedom, enabling one to become a true “global citizen.”
What is the Difference Between Citizenship and Permanent Residency?
Citizenship grants more rights, including a passport from the country, while permanent residency allows you to live and travel in the country without a visa and to stay there for an extended period, provided you follow the rules and pay taxes.
Unlike citizens, permanent residents do not have political rights, such as voting or participating in elections. They remain citizens of their home country and can only obtain political rights through dual citizenship or, in some countries, by renouncing their original citizenship.
Which Countries Recognize Dual Citizenship?
Most countries that allow dual citizenship are located in Europe, such asPortugal,France,Italy,Malta, and others. However, dual citizenship is also permitted in countries in North and Latin America. This does not mean that no African or Asian countries allow dual citizenship.
Full list of countries that allow dual citizenship
*however, it is important to note that the rules for dual citizenship can vary significantly depending on the country, and some impose strict conditions for obtaining it.
It is worth noting that many countries grant their citizenship and passport if you were born on their territory. This is a straightforward path to obtaining dual citizenship in many countries. For example, if a personwas born in the USA, they automatically receive their citizenship and passport, making them a citizen of one of the countries with the best passports in the world.
In Which Countries is Multiple Citizenship Allowed?
Generally, any country that allows its citizens to hold dual citizenship also permits them to have more than two citizenships, enabling them to become not just dual citizens but global citizens.
Migronis experts will help you choose the country that best suits your needs and budget.
Discover more about available options and receive personalized advice.
Which Countries Allow Dual Citizenship with the USA?
The USA, one of the largest countries in North America, allows its citizens to hold dual citizenship. This means that US citizenship is not revoked when acquiring citizenship from another country, provided that country also permits dual citizenship. This fact makes the USA attractive to individuals who want to benefit from the advantages of two or more countries simultaneously, seeking freedom of movement and tax benefits.
However, it is important to remember that not all countries allow their citizens to retain a second citizenship.
Countries Allowing Dual Citizenship
Most countries that permit dual citizenship do not have restrictions on combining it with US citizenship. For example, European Union countries such as Portugal, Malta, France, and Italy recognize dual citizenship.
However, there are exceptions, such as Spain, which only allows dual citizenship for citizens of certain countries, such as Latin American countries. Therefore, for Spaniards, acquiring US citizenship may lead tolosing Spanish citizenship, although the USA continues to recognize their dual citizenship.
US Tax System
An important aspect of obtaining US citizenship is understanding the country’s tax system. US citizens must pay taxes on all income, regardless of their country of residence. This can include income earned abroad, making the US tax system one of the strictest in the world.
Many seek second citizenship in countries with more favorable tax conditions, such as Portugal or Malta, to reduce their tax burden.
Countries That Do Not Allow Dual Citizenship
Some countries prohibit dual citizenship, and in some cases, it can be considered a criminal offense. Most of these countries are located in Asia, particularly in the Persian Gulf and Central Asia regions, as well as in Africa.
Countries That Completely Ban Dual Citizenship:
|
Afghanistan |
El Salvador |
Lithuania |
Singapore |
|
Andorra |
Estonia |
Malaysia |
Slovakia* |
|
Austria |
Georgia |
Montenegro |
Tanzania |
|
Azerbaijan |
India |
Netherlands* |
Thailand |
|
Bahrain |
Indonesia |
Nepal |
Ukraine |
|
China |
Japan |
Poland |
Venezuela |
|
Djibouti |
Kazakhstan |
Saudi Arabia |
*some countries, such as Slovakia and the Netherlands, allow dual citizenship under certain circumstances.
Investment Citizenship Programs
This is the simplest way to obtain a second passport by investing in the economy of another country. These programs allow foreign nationals to contribute to the development of a country through various forms of investment, such as purchasing real estate, starting a business, or buying government bonds. In return, investors receive citizenship and all associated benefits, including the right to reside, work, and travel visa-free to certain countries.
Key Investment Citizenship Programs:
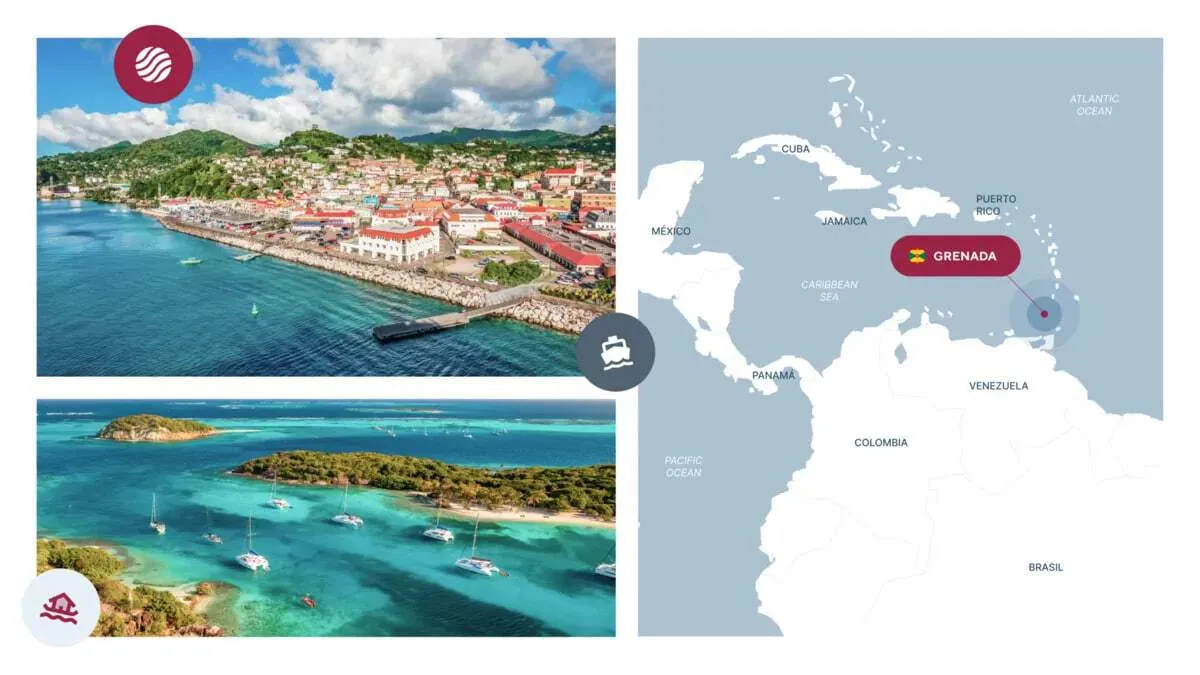
Grenada
- Processing Time: 6-10 months
- Minimum Investment: $235,000
- Simplified Entry: 156 countries
- Passport Validity: 10 years
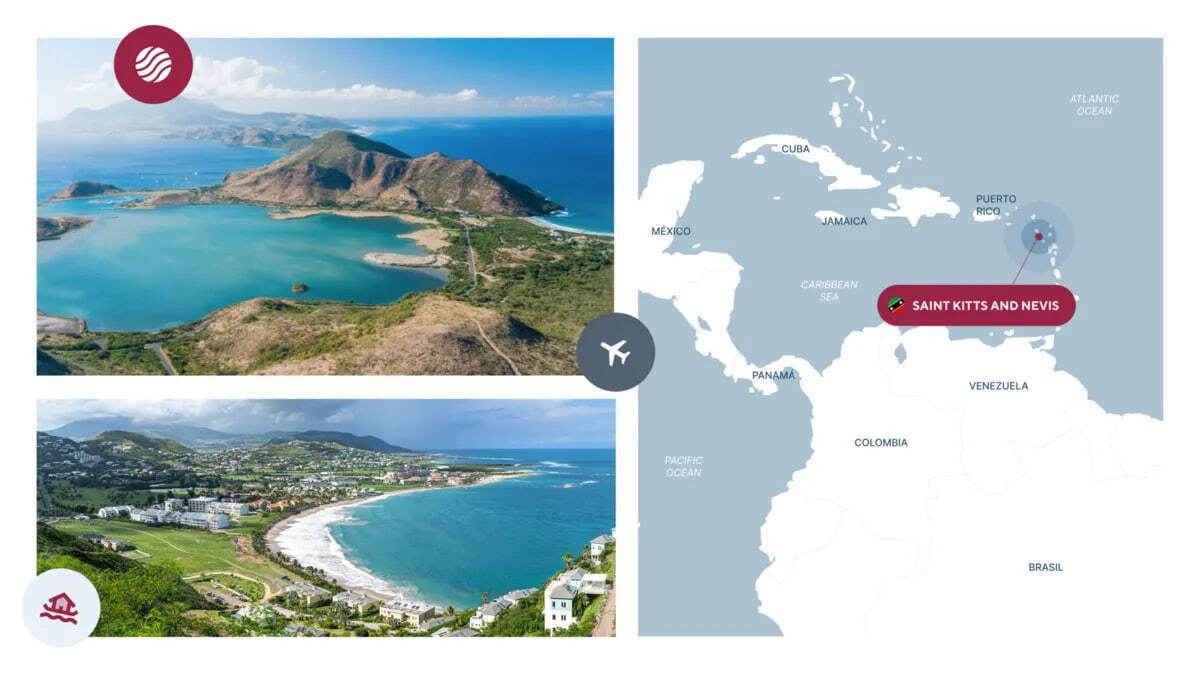
Saint Kitts and Nevis
- Processing Time: 6-8 months
- Minimum Investment: $250,000
- Passport Validity: 10 years (5 years for children)
- Simplified Entry: 160 countries
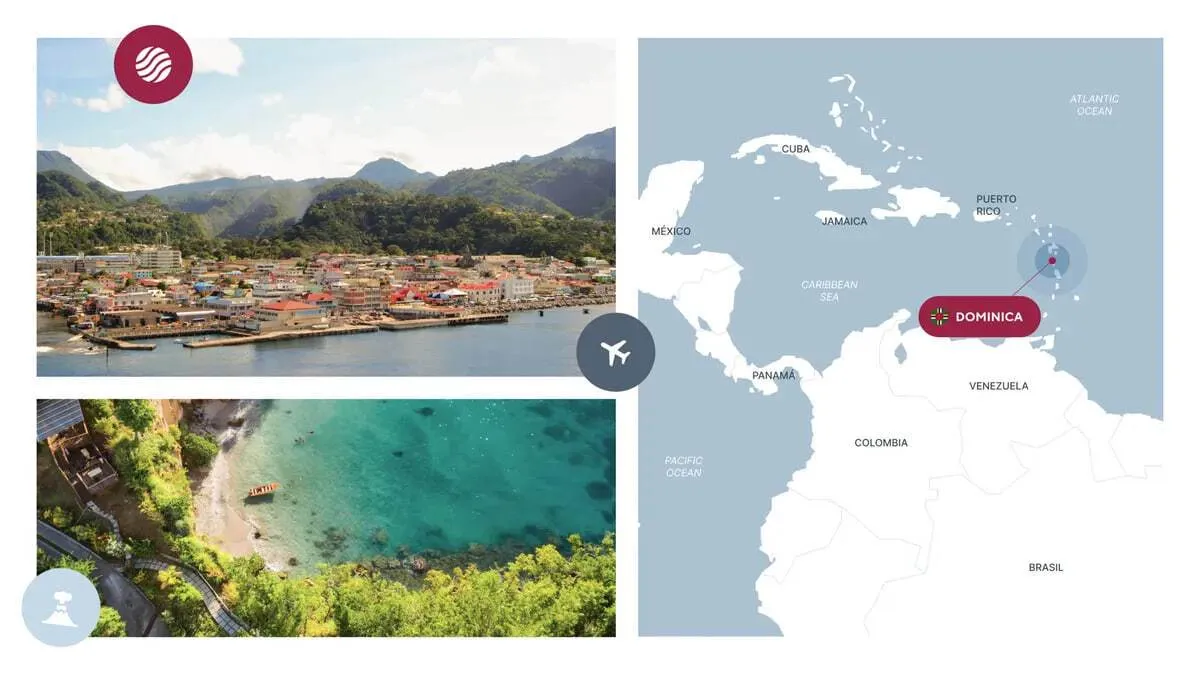
Dominica
- Processing Time: 4-6 months
- Minimum Investment: $200,000
- Simplified Entry: Over 153 countries
- Passport Validity: 10 years
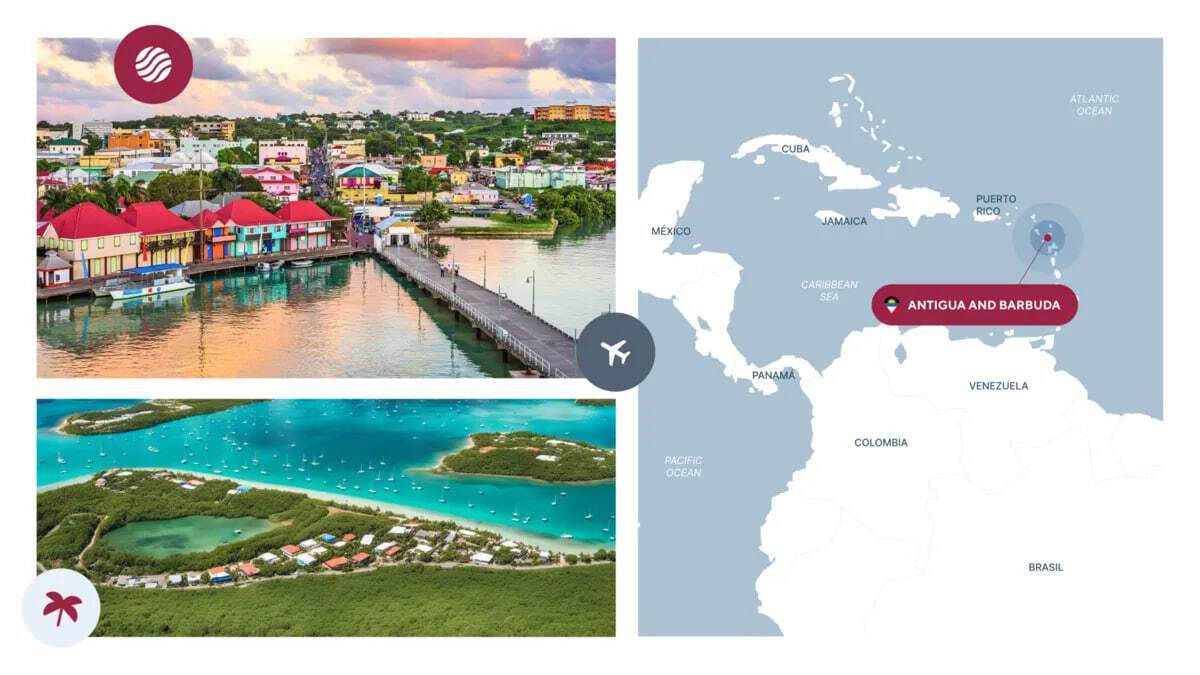
Antigua and Barbuda
- Processing Time: 4-6 months
- Minimum Investment: $230,000
- Simplified Entry: 158 countries
- Passport Validity: 10 years
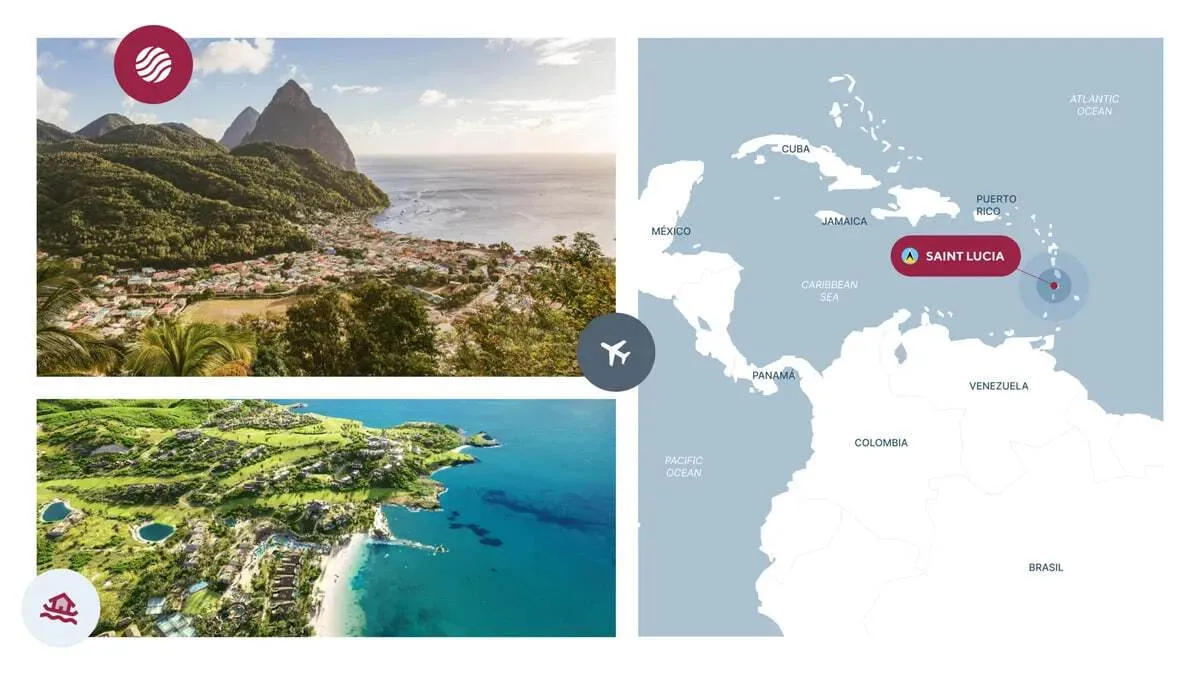
Saint Lucia
- Processing Time: 6-10 months
- Minimum Investment: $240,000
- Passport Validity: 5 years
- Simplified Entry: 155 countries
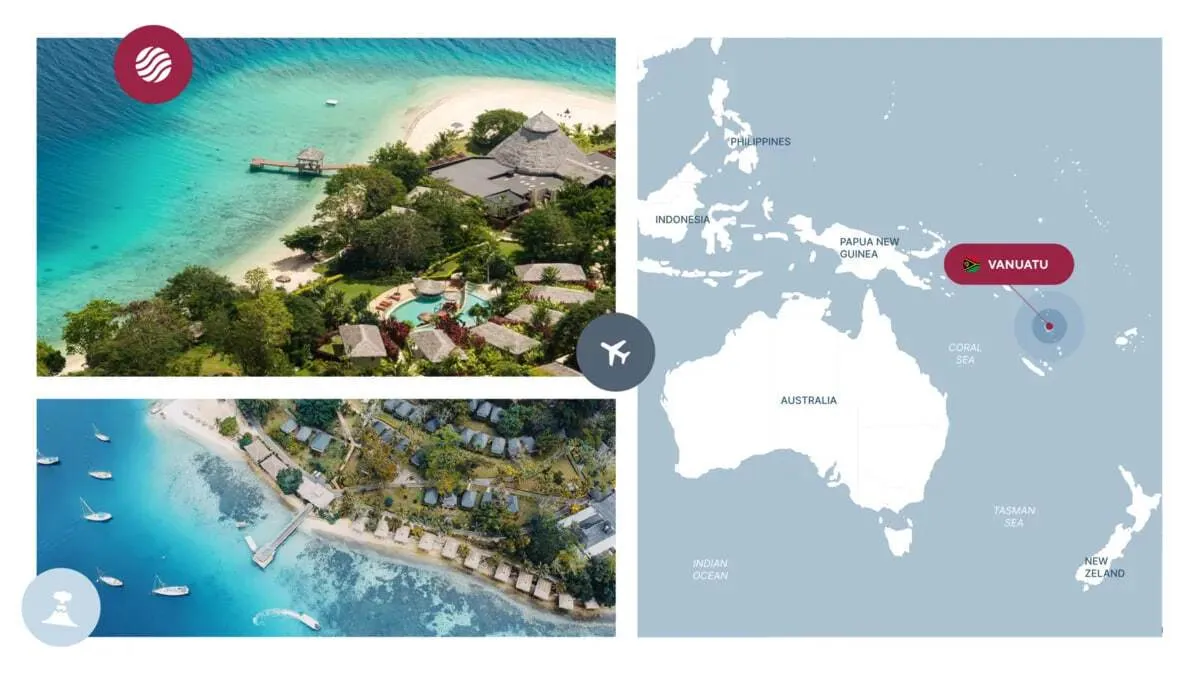
Vanuatu
- Processing Time: 1-3 months
- Minimum Investment: $130,000
- Passport Validity: 10 years
- Simplified Entry: 125 countries
Each program has its own requirements, application process, and processing times, allowing investors to choose the most suitable option based on their goals and resources. Your country of birth is not an obstacle when it comes to these programs, making your options quite abundant.
Migronis experts are ready to help you select the perfect program that best matches your goals and budget. Our experience and knowledge in international law will ensure a seamless citizenship acquisition process.
Contact us today to start your journey to new citizenship!